Sensational Info About Does A Car Use AC Or DC Power

AC Vs. DC Electric Car Charging YouTube
The Great Car Power Debate
1. Understanding the Electrical Heart of Your Ride
Ever wondered what makes all those electrical gadgets in your car tick? We're talking headlights, your phone charger, that oh-so-necessary heated seat on a chilly morning — the list goes on! The answer, like many things in the automotive world, isn't quite as straightforward as you might think. It's not simply an AC or DC situation; it's more of a carefully orchestrated power ballet. Think of it as an electrical ecosystem under your hood.
Initially, cars primarily relied on DC (Direct Current) power. This is because batteries, the energy storage workhorses, provide DC. So, for years, pretty much everything ran directly off the battery's consistent flow of electrons. Simple, right? Well, not quite!
As technology advanced, and we started demanding more sophisticated features in our vehicles (think complex engine management systems, entertainment units, and those delightful automatic windows), the need for AC (Alternating Current) components started creeping in. AC offers certain advantages for specific applications, particularly those involving motors and power conversion. Plus, who doesn't love blasting their favorite tunes on a long drive?
So, how do these two power types coexist peacefully within your four-wheeled friend? Let's dive deeper into the electrifying details!
![EV Charging The Difference Between AC And DC [2023 Update] EV Charging The Difference Between AC And DC [2023 Update]](https://blog.evbox.com/hs-fs/hubfs/Difference AC DC_2.png?width=1280&height=720&name=Difference AC DC_2.png)
EV Charging The Difference Between AC And DC [2023 Update]
DC
2. The Unwavering Source of Automotive Energy
DC, provided by your car's battery, is the bedrock of its electrical system. The battery supplies the initial energy for starting the engine and powering essential components like the ignition system and the engine control unit (ECU). It's the unsung hero that gets you going every single time you turn the key (or push the button, if you're fancy!).
Beyond starting the engine, DC power keeps the lights on — literally. Your headlights, taillights, brake lights, and interior lights all rely on the battery's steady DC current. It also powers essential safety features like airbags and anti-lock brakes (ABS), ensuring your safety on the road.
Even some of the more modern conveniences, like power windows and door locks, operate on DC. Essentially, anything that needs a consistent and reliable power source is likely running on good old DC. It's the reliable friend you can always count on, always ready to power the essentials.
Think of DC as the foundation upon which the rest of the car's electrical system is built. It's the constant, the reliable, the always-there power source that makes everything else possible.
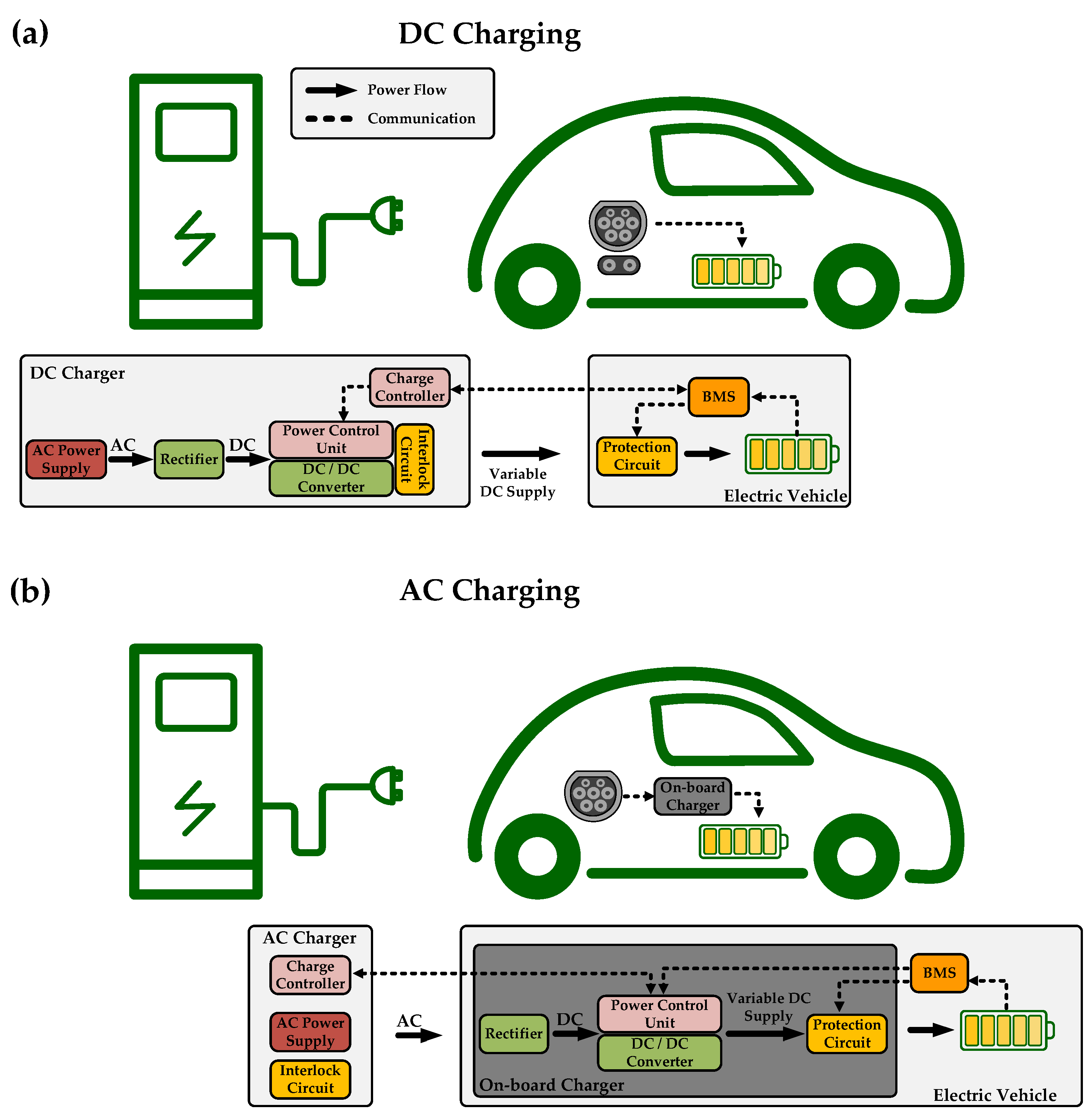
Energies Free FullText Current Trends In Electric Vehicle Charging
AC
3. Where Alternating Current Shines in Automotive Applications
While DC holds the primary role, AC has found its niche in specific areas within your car. The most common example is the alternator. The alternator, driven by the engine, generates AC power. But wait, wasn't DC supposed to be king? Don't worry, there's a method to this madness.
The alternator's AC output isn't used directly to power components. Instead, it's immediately converted to DC using a rectifier. This converted DC then recharges the battery and supplements the battery's power when the engine is running. Think of the alternator as the battery's personal trainer, constantly keeping it in shape.
Why not just generate DC directly? Because it's more efficient to generate AC and then convert it to DC for this specific purpose. The design and operation of an alternator are better suited for producing AC power at varying engine speeds. It's all about optimizing efficiency and performance.
Looking to the future, with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), AC is playing an even bigger role. EV charging stations often supply AC power, which the car then converts to DC to charge the battery pack. So, while DC remains fundamental, AC's influence is undeniably growing in the automotive landscape.
DC Motors
The Conversion Dance
4. How Your Car Manages Different Power Types
The real magic happens in the conversion process. As we've seen, the alternator produces AC, which is then converted to DC to charge the battery and power the electrical system. This conversion is achieved using a device called a rectifier, essentially an electronic one-way valve for electricity.
But the conversion doesn't always flow in just one direction. Sometimes, DC needs to be converted back to AC. For example, some advanced audio systems use inverters to convert the car's DC power into AC to drive specific components for optimal sound quality. It's all about getting the right type of power to the right place at the right time.
These conversions are managed by sophisticated electronic control units that constantly monitor and adjust the flow of power throughout the vehicle. It's a complex and dynamic system that ensures all the electrical components receive the power they need to function correctly. Think of it as a meticulously choreographed electrical dance.
Understanding this conversion process is key to understanding the car's overall electrical architecture. It highlights the interplay between AC and DC and how they work together to keep your car running smoothly and powering all your favorite gadgets.

The Future of Automotive Power
5. Exploring the Shift Towards Advanced Electrical Systems
As vehicles become increasingly electrified, with more features and advanced technologies, the role of AC is likely to expand. Electric vehicles, in particular, rely heavily on AC for charging and powering various systems. The trend towards higher voltage systems also favors AC for efficiency reasons.
Furthermore, the development of more sophisticated power electronics is enabling more efficient and reliable AC-DC conversion. This means that future cars could potentially utilize AC power for a wider range of applications, leading to improved performance and energy efficiency. It's an exciting time for automotive electrical engineering!
The adoption of 48V electrical systems is another trend that could influence the balance between AC and DC. These higher voltage systems can handle more power and are better suited for supporting power-hungry features like advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and electric power steering. While still primarily DC-based, these systems may incorporate more AC components for specific tasks.
So, while DC will undoubtedly remain a core component of automotive electrical systems, the future seems to be pointing towards a greater integration of AC, driven by the increasing demand for power and the advancements in power electronics. The power ballet is only going to get more complex and fascinating!
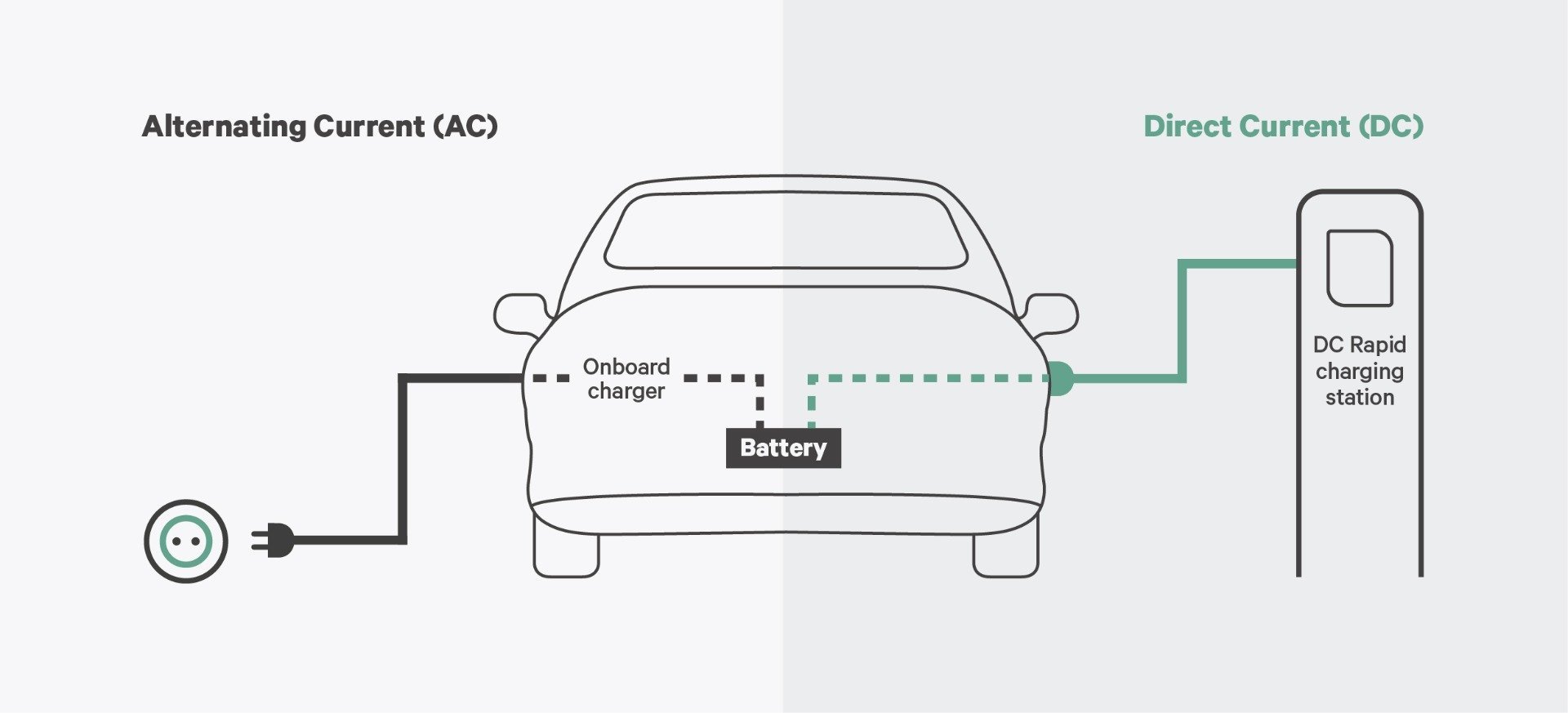
Charging Your EV In Malaysia AC Vs DC
FAQ
6. Q
A: Primarily DC. The battery provides DC power for starting the engine and running most of the car's essential components. AC is generated by the alternator but is immediately converted to DC to recharge the battery.
7. Q
A: It's all about efficiency and practicality! DC is great for batteries and many electronic components, while AC is more efficient for generating power at varying engine speeds. The conversion between the two allows the car to optimize power usage for different functions.
8. Q
A: Absolutely! Electric vehicles rely heavily on AC for charging, as most charging stations supply AC power. The EV then converts this AC to DC to charge the battery pack. The electric motors in EVs also often use AC power, although this is usually converted from DC from the battery.